December 18, 2023
Picture this…
…it’s 1920, and you’re about to witness a pivotal moment in medical history orchestrated by the brilliant mind of Canadian surgeon Frederick Banting. Armed with a groundbreaking theory, Banting reaches out to John Macleod, a forward-thinking professor at the University of Toronto. Now, Macleod isn’t your average academic; he’s a guy who sees the potential in disruptive ideas. Not only does he swing open the doors to the university’s labs, but he also provides Banting with the equipment he needs and a savvy research student named Charles Best to join the experiment.
After three years of intense experimentation, Banting and Macleod walked away with the 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Their crowning achievement?
Insulin – the first commercial peptide and a game-changer in the realm of medicine.
So, what are peptides, exactly?
Peptides are amino acid-crafted messengers that assist in tasks like tissue repair and cognitive function. Naturally produced by the body and also synthetically created by scientists for potential health benefits, peptides act as precision tools in cellular communication.
These transformative game-changers are an invaluable asset in the landscape of wellness, which is why I’m unveiling my top peptide stacks embraced by health enthusiasts for goals like enhancing physical performance, optimizing cognitive function, and unlocking the secrets of sustained vitality. Embark on a deep dive into fundamental peptide aspects, exploring their roles, benefits, and the scientific foundations that position them as catalysts for redefining approaches to health and longevity.
Stay tuned as the science behind peptides unravels, paving the way for a revolution in your well-being.
What Is a Peptide?
A peptide is a short chain of amino acids, serving as a crucial molecular messenger in the body — falling between individual amino acids and longer protein chains. Functioning as signaling molecules, peptides play a pivotal role in diverse biological processes, including tissue repair, cognitive function, and energy regulation.
The human body naturally produces many peptides, but because peptides are so simple to reproduce and create, synthetic versions, usually designed and produced in labs by linking specific amino acids together, can replicate benefits like enhanced sleep, body composition improvements, and support in injury recovery.
What Is a “Peptide Stack”?
As you venture into the fascinating realm of peptides, you’ll frequently notice health enthusiasts and biohackers using the term “peptide stacking.” Now, I get it might sound like I’m bombarding you with a slew of definitions, but hang tight with me for a moment — I want to ensure you’ve received a straightforward breakdown of important terms before we plunge into the peptide rabbit hole.
Okay, so what is a peptide stack?
Generally speaking, a supplement “stack” refers to the combination of different dietary supplements taken together to enhance or complement each other’s effects. Examples of popular stacks include creatine + amino acids, which is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts for its potential to enhance muscle growth; fish oil + nootropics (cognitive enhancers), which can support brain health and cognitive function; and niacin + lion’s mane, used for neuroprotective and cognitive benefits.
The concept behind a peptide stack is to amplify the overall effectiveness of peptides, targeting multiple health goals simultaneously. Whether the goal is to enhance physical performance, optimize cognitive function, or achieve other specific outcomes, a well-designed peptide stack aims to harness the collective power of these bioactive molecules for comprehensive health optimization.
In short, peptide stacking isn’t just about throwing together a random mix; it’s about crafting a personalized health strategy and unlocking the magic that happens when specific peptides team up.
It’s a superhero ensemble for your health — intentionally combining forces to tackle multiple goals at once, cranking up the overall effectiveness. Imagine one peptide playing the role of an anti-inflammatory agent, while another steps in to amp up muscle growth or sharpen your cognitive edge.
Whether you’re delving into the best anti-aging practices, looking to elevate your fitness game, seeking faster recovery, or aiming for a state of overall well-being, your peptide stack is as individual as you are. There’s no universal stack here — it’s about finding what works for you, your body, and your health journey.
For more background on peptide basics, check out my other articles, podcast episodes, and this list of resources:
- “Everything You Need To Know About Peptides Part 1: What Are Peptides, Where to Get Peptides, How To Reconstitute Peptides, Peptide Storage, Peptide Injections & More!”
- “Everything You Need To Know About Peptides Part 2: The Best Peptide “Stacks” for Everything from Recovery to Fat Loss, Muscle Gain, Immunity, Anti-Aging, and More.”
- “Everything You Need To Know About Peptides Part 3: Are They Safe? Are They Legal? & Other Frequently Asked Questions About Peptides.”
- “The Peptides Podcast: Everything You Need To Know About Anti-Aging, Muscle Gain, Fat Loss & Recovery Peptides.”
- “Is Metformin Really Dangerous, Little-Known Peptides For Muscle Gain & Fat Loss,”
- “Peptides Unveiled: The Best Peptide Stacks For Anti-Aging, Growth Hormone, Deep Sleep, Hair Loss, Enhanced Cognition & Much More!”
- Ben Greenfield’s Ultimate Peptides Resources Page
How Do Peptides Work?
Peptides work like tiny messengers in your body, telling your cells what to do so they can perform important tasks.
In essence, you can use peptides to replicate processes your body already carries out, such as healing injuries or making new cells. Supplementing with peptides helps cells do their job and keeps your body in homeostasis (balance). Think of using peptide stacks like giving your body instructions on how to keep everything running smoothly.
Peptides exhibit a remarkable specificity in targeting physiological functions, significantly mitigating the likelihood of adverse effects. Biologically, peptides demonstrate a chameleon-esque versatility, functioning as hormones, neurotransmitters, enzymes, and comprehensive regulatory molecules, thereby playing a key role in managing many important functions in the body.
Visualize each peptide as a specialized key designed to fit perfectly into specific locks — which are cell receptors. When a peptide binds to its corresponding receptor, it’s like turning a key that initiates a cascade of cellular responses that fine-tune our body’s complex systems. This binding process triggers various actions within the cell, depending on the type of peptide and receptor involved. It could signal a cell to repair itself, kickstart the production of a hormone, or even instruct a cell to turn certain genes on or off. It’s this precise interaction that allows peptides to influence such a wide range of bodily functions.
Examples of Well-Known Peptides
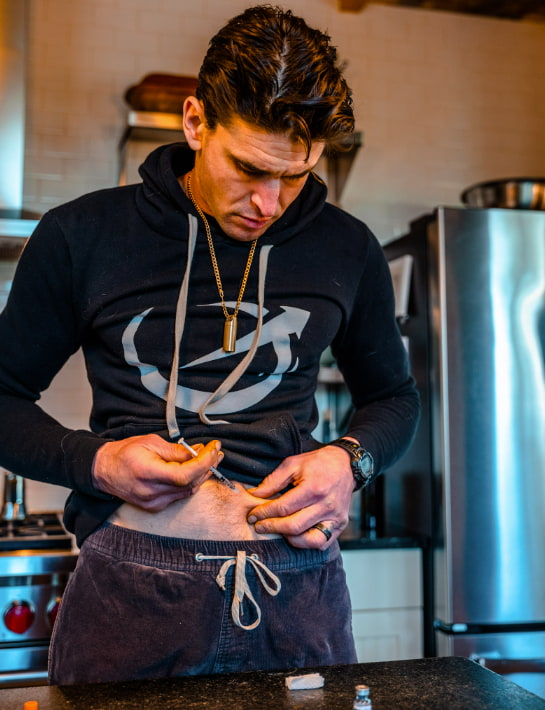 There are many different types of peptides with diverse structures, functions, and mechanisms of action.
There are many different types of peptides with diverse structures, functions, and mechanisms of action.
For example, one type you’re likely familiar with is collagen, which is a peptide often touted for its ability to improve the appearance and integrity of skin and joints. Biologically, collagen works by forming a sturdy, fibrous network in tissues, giving them structure and resilience while also playing a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration by providing a scaffold for new cell growth.
Other examples of peptides include Human Growth Hormone (HGH), BPC-157 (known for its powerful healing properties), TB-500 (used to help reduce inflammation), and CJC-1295 (used to aid in muscle growth and fat loss). For a more thorough explanation of different peptides and their uses, check out my article on the best peptide stacks for recovery, fat loss, and anti-aging.
Yet another big name in the peptide world that you’re probably hearing a lot about is Semaglutide (or Ozempic), which is the synthetic version of a naturally occurring human hormone called Glucagon-like peptide-1 or GLP-1. This peptide, now commonly taken as a weight loss drug, helps to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce hunger, therefore helping people manage their weight.
While its effects have been compared to those of bariatric surgery, I have some serious concerns about the long-term use of Semaglutide (considering that it can reduce lean muscle mass and strength, in addition to potentially having a lifespan-lowering effect). Sure, it can offer a scientific nudge for those resistant to shedding pounds, but — and this is a colossal “but” — the risks of Ozempic read like a cautionary tale, from “possible thyroid tumors, including cancer” to “inflammation of the pancreas,” “changes in vision,” “low blood sugar,” “kidney problems (kidney failure),” and a parade of side effects like nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and serious allergic reactions.
Considering the risks, does this logically sound like a wise choice for the general populace? I’m inclined to think not. It may not be the effortless route, but the far superior strategy for sustained weight loss lies in cultivating a disciplined mindset, exercising self-control, and building character through a commitment to regular exercise and wholesome nutrition. Just my two cents for optimizing longevity, health, wellness, and happiness, unless you happen to be genetically predisposed to the weight loss struggle — in which case, a nuanced approach might be in order.
What Are the Health Benefits of Peptides and Peptide Stacks?
Peptides are like the Swiss Army knives of your body’s toolkit — especially when you cleverly stack them. From regulating physiological processes to their superhero-like presence in medicine and skincare, these tiny wonders are a powerhouse. Yet, trying to give you the full scoop on what peptides can achieve for your health and appearance is like attempting to condense a library into a tweet.
That said, here’s a basic rundown of some key benefits associated with peptides and peptide stacks:
- Improved brain health and cognitive performance
- Contribution to longevity
- Promotion of tissue healing and reduction of inflammation, aiding in injury recovery
- Stimulation of growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration
- Support for wound healing and skin renewal
- Facilitation of growth hormone release, aiding in muscle growth and fat loss
- Assistance in immune system responses and defenses and combatting skin infections
- Regulation of blood sugar levels, glucose/energy utilization, insulin release, and fat storage
- Maintenance of normal fluid levels
What Anti-Aging Effects Do Peptides Have (Including for Skin)?
If you’re eager to harness the power of peptides to reverse the aging clock, peptide stacks offer a bespoke approach to target specific anti-aging goals, whether it’s revitalizing skin health or expediting injury recovery. With their remarkable versatility and efficacy, peptides have become a go-to choice for redefining the limits of human performance and health, especially as you age.
One of the most popular uses for peptides is in skin care since they can have significant anti-aging effects on the skin. This is why you’ll find peptides in products such as serums and face creams intended to support collagen production and regulate fibroblasts. One study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that a specific peptide complex can improve skin structure and reduce wrinkles by stimulating key proteins at the skin’s dermal-epidermal junction.
Peptides also help with anti-aging effects on the skin by:
- Stimulating Collagen Production: Certain peptides, known as collagen-stimulating peptides, can signal the skin to produce more collagen. This helps reduce the appearance of wrinkles and improves skin texture.
- Enhancing Integrity of the Skin Barrier: Peptides can strengthen the skin’s barrier function, which tends to weaken with age. A stronger barrier helps retain moisture, protect against environmental damage, and maintain overall skin health.
- Promoting Elastin Production: Some peptides help boost the production of elastin, an important protein in the skin that maintains its elasticity, keeps skin supple, and reduces sagging.
- Providing Antioxidant Effects: Peptides can also have antioxidant properties, meaning they can neutralize free radicals in the skin that can cause oxidative stress, leading to premature aging of the skin.
- Improving Skin Hydration: Peptides can enhance the skin’s natural hydration mechanisms, which often become less efficient with age. Well-hydrated skin appears plumper, smoother, and more youthful.
- Regulating Pigmentation: Some peptides can influence melanin production in the skin, helping to reduce age spots and hyperpigmentation and even out skin tone.
Are Some Peptides Illegal?
Most peptides themselves are not “illegal”; however, their regulation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is complex and depends on the specific peptide and its intended use.
Historically, peptides such as insulin have been therapeutic mainstays that are widely available. In fact, in the U.S., over 100 peptide drugs are approved for use. Recent advancements have further amplified the therapeutic potency and accessibility of some peptides, but at the same time, the emerging use of peptides has raised concerns about the quality and safety of certain types when sold commercially to the public.
Here’s a quick summary of how the FDA labels peptides:
- Therapeutic Peptides: A number of peptides are used therapeutically and are FDA-approved for specific medical conditions. An example is insulin, which is used for diabetes, or Semegalutide, which is used for diabetes and obesity.
- Research Peptides: Some peptides are available for “research purposes only” and are not FDA-approved for human consumption. This is a gray area where peptides are manufactured and sold for laboratory research but not for personal use.
- Cosmetic Peptides: In the realm of cosmetics, peptides are used in skin care products for their potential anti-aging, healing, or rejuvenating properties. These are generally legal and regulated as cosmetics, not as drugs.
- Dietary Supplements: Peptides marketed as dietary supplements are subject to FDA oversight, so the FDA does not approve them or ensure that they’re safe.
- Banned or Controlled Peptides: Some peptides are considered Schedule 2 substances that are banned or controlled due to potential side effects or abuse, particularly in professional sports.
Do Certain Peptides Lack FDA Approval Because They’re Dangerous?
So are peptides now being cracked down on by the FDA because peptides are dangerous?
Not necessarily.
Many peptides aren’t technically FDA-approved because they aren’t patentable; therefore you won’t see them recommended by most mainstream health authorities or mentioned on most health websites. Issues surrounding patents are a big deal in the peptide space.
Unless a drug company is going to be able to patent a peptide, turn it into a drug, and make a lot of money from doing so, they aren’t going to waste time, funds, and effort having the peptide be FDA-approved. Therefore, most peptides are not FDA-approved and likely won’t be in the foreseeable future.
Even the FDA itself has issued cautionary warning letters to compounding pharmacies pointing out that certain peptides cannot be compounded legally because they don’t have a monograph in the US Pharmacopeia or National Formulary, aren’t part of any drug approved by the FDA for human use, and aren’t included in the 503A list of bulk substances.
While most peptides are not outright illegal, their legal status depends on their intended use, claims made about them, and whether they are FDA-approved for that specific use.
Why Was BPC-157 Banned by the FDA?
There have been instances where the FDA has cracked down on the sale and use of certain peptides that are not approved for human use, particularly those sold online for self-administration. In October 2023, the FDA made some updates to its list of bulk drug substances, classifying some peptides as off-limits.
BPC-157, a peptide known for its joint healing properties and ability to fight inflammation, was banned by the FDA for general use, restricting it to “research purposes only.” This came after research demonstrated that BPC-157 has anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and endothelial-protective effects in different organ systems, to the extent that it may even help treat COVID-19.
The ban (under Sections 503A or 503B of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act) was primarily due to concerns over its safety and the lack of clinical trials to establish its efficacy and potential side effects.
So, while the FDA hasn’t yet declared BPC-157 safe for public use, it may become legal in the future depending on how much rigorous testing is done.
Given that BPC-157 did show promise for mitigating inflammation and supporting tissue healing, its status could potentially change if trials show its benefits outweigh its potential risks.
Can You Still Get Peptides, And If So, Where?
As you can see, when it comes to using peptide stacks for biohacking, or what the FDA calls “compounded drugs,” things get a bit tricky. Most peptides are not FDA-approved, which means they haven’t undergone the FDA’s rigorous review process for safety, effectiveness, and quality.
Given the unregulated nature of peptides and their exclusion from FDA approval, sourcing them can be challenging. You do have the option to obtain FDA-approved peptides (such as Semaglutide, which pulled in more than $23 billion in revenue in 2023) with a prescription. For those that aren’t approved, obtaining them through reputable healthcare providers or trusted online sources is your best bet, ensuring quality and safety.
I recommend sourcing peptides from some of these trustworthy brands (you can check out my Peptides Resources Page for discounts):
You can visit a healthcare provider to receive certain peptides that are still legal to purchase for human use but may require a prescription. Currently, these include the following types:
- Sermorelin
- PT-141
- Tirzepatide
- Semaglutide
If you’d like to dive deeper into information about peptides other than those that are currently legal, you’ll want to check out research websites such as:
How Are Peptide Stacks Used?
In general, peptide stacks aren’t used like other supplements or even medications. For example, many are injected, and some are only used once per week for several
weeks at a time, a few times per year. This frequency of peptide stacks might not seem like a lot, but it’s enough to provide significant results.
The dosage and timing of each peptide in a stack are crucial, so don’t overlook specific instructions about how to use peptides. Incorrect dosages or timing can not only diminish the effectiveness of the stack but also increase the risk of side effects.
Many peptides also require “breaks” in which you stop using them for several weeks or longer to allow your body to safely adjust to their effects.
Can you stack peptides in any combination you’d like? While there is some flexibility in creating peptide stacks, it should be done thoughtfully and ideally under the guidance of a knowledgeable healthcare provider. You want to avoid combining peptides that might have conflicting or counterproductive effects.
Definitely speak with a provider before using peptide stacks if you have allergies or take daily medications. And finally, always source peptides from reputable suppliers so you know for sure that you’re getting the best quality and purity.
What Are a Few of the Best Peptide Stacks?
If you’re curious about peptide stacks and where to source them, chances are you’re looking for answers to these questions that I get all the time…
“What’s the best peptide stack for fat loss?”
“Which peptide stacks help build lean muscle mass?”
“What peptide stack is most like testosterone or HGH?”
I’ve discussed my favorite peptide stacks many times in the past (for example, here on my Ultimate Peptide Resources Page and also with Jay Campbell). So, in the spirit of not reinventing the wheel, I recommend the following peptide stacks for various purposes:
Sample Stack for Full Body Optimization (Lean Muscle Gain, Fat Loss, General Health, Anti-Aging, and Longevity):
- Melanotan-1: 500 mcg injected subcutaneously three times a week, with the doses evenly spaced out within the week.
- Thymosin Alpha-1: 1.5 mg injected subcutaneously once per day if traveling, once per day if recovering from an illness, and every other day in normal circumstances.
- BPC-157 & TB-500: Take this only when seriously hurt. Administer 200–750 mcg of BPC-157 injected locally at the site of injury, intramuscularly or subcutaneously, once in the morning and once at night. Administer 2.5–3.0 mg of TB-500 injected locally at the site of injury, intramuscularly or subcutaneously, once a day in the morning or at night (but at the same time as your BPC-157 injection). Continue this protocol for a maximum of 12 weeks or until the injury is 100% healed.
- Tesofesnsine: One 0.5 mg tablet immediately in the morning while in a fasted state. Continue this every day until your fat loss cycle is complete (it may not produce results until six months into use).
- Semaglutide: 0.25 mg injected subcutaneously once a week (preferably on a day you are eating and training). Gradually increase the dose every four weeks up to a maximum of 2.4 mg or until you experience desired appetite-suppressing effects.
Sample Stack for Muscle Growth:
- 5-Amino 1MQ: One capsule taken by mouth per day in the morning. Take it for two days on, two days off for a total of 8–10 weeks.
- CJC-1295 (without DAC): In the morning, take 200 mcg injected subcutaneously every day on. Take for five days, then break for two days. Follow this schedule for 8–10 weeks. Then, take a break for 8–10 weeks before repeating the cycle.
- Ipamorelin: In the morning, take 200 mcg injected subcutaneously every day on a five days on, two days off schedule for 8–10 weeks. Then, take a break for 8–10 weeks before repeating the cycle.
- Tesamorelin: In the evening, take 1mg injected subcutaneously every day on a five days on, two days off schedule for 8–10 weeks. Then, take a break for 8–10 weeks before repeating the cycle.
Sample Stack for Fat Loss and Getting Lean:
- Semaglutide: 0.25 mg injected subcutaneously once a week, increasing by 0.25 mg every 4 weeks up to a maximum of 2.4 mg.
- AOD-9604: 300 mcg injected subcutaneously once a day in the morning while fasted (ideally administer it one hour before the first meal of the day or right before doing cardio).
- Ipamorelin: In the morning, inject 200 mcg subcutaneously every day on a five day on, two days off schedule for 8–10 weeks. Then, take a break for 8–10 weeks before repeating the cycle.
- Tesamorelin: In the evening, inject 1 mg subcutaneously every day on a five days on, two days off schedule for 8–10 weeks. Then, take a break for 8–10 weeks before repeating the cycle.
Sample Stack for Help Recovering From Injuries:
Morning:
- Ipamorelin: 200–300 mcg
- TB-500: 2.0–2.5 mg
- BPC-157: 250 mcg
Evening:
- Tesamorelin: 1 mg
- BPC-157: 250 mcg
Sample Stack for Brain Health:
- RG3: 1–2 sprays nasally, preferably combined with NAD and vitamin B12.
- DIHEXA: 1–2 sprays nasally.
- Semax: 1–2 sprays nasally.
- Selank: 1–2 sprays nasally.
For help learning how to reconstitute peptides and administer them subcutaneously and intramuscularly, check out this article.
Summary
Peptides aren’t just a fleeting health trend — they represent the forefront of groundbreaking innovation in the pursuit of optimal health and wellness. As I wrap up this enlightening exploration, consider it not a conclusion but an initiation into a realm of boundless potential. For those eager to dive deeper into the world of peptide stacks, explore my extensive collection of resources, including articles and podcast episodes, for in-depth insights, tips, and updates on the latest in peptide research and applications. Instead:
- Peptides offer a promising avenue for those looking to enhance their health, longevity, and performance, especially when used in stacks, which amplifies their effects.
- As research continues to evolve, peptides are likely to become an even more integral part of anti-aging therapies and injury recovery.
- While their potential is immense, it’s important to approach the use of peptide stacks with caution, considering that many aren’t FDA-approved or widely available by mainstream healthcare providers.
- Be sure to seek out quality peptides from trustworthy brands, follow directions carefully, and ideally, work with a provider who has experience administering peptides.
I encourage you to start with my Ultimate Peptide Resources Page or by checking out this *epic* deal from Limitless Life Nootropics to experience the “limitless” possibilities in health and wellness. Click here to gain access to their nootropic supplements (including exclusive discounts on some of the peptides discussed in this article). Use code GREENFIELD 20% for regular products and 10% for VIP products (offer valid until December 31st).
Want to continue exploring all things peptides? Discover more here:
Peptide Three-Part Article Series:
Peptide Podcast Episodes:
Disclaimer: I am not a doctor and this is not to be taken, interpreted, or construed as medical advice. These are just my own personal thoughts and not a prescription or a diagnosis or any form of health care whatsoever. Please talk with a licensed medical professional if you’re interested in using peptides. In addition, most of this stuff is banned by the World Anti-Doping Association (WADA), US Anti-Doping Association (USADA), and other international governing bodies of sport, so you should not use any of these compounds if you are competing in any sanctioned sport. You can click here to search for whether peptides (or other compounds) are legal in your sport. Also, please note that the world of peptides is ever-evolving, and while I do try to keep posted articles updated, I can only attest that this information is current as of December 2023.